our solutions
OTT
OTT
OTT (Over-The-Top) refers to internet-based content delivery without cable or satellite TV. It offers diverse content accessible on various devices globally. Most OTT platforms operate on a subscription model, providing on-demand and live content. Original programming and personalized recommendations are common features. Popular platforms include Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, Disney+, and YouTube Premium, transforming media consumption. OTT’s convenience and flexibility have revolutionized the entertainment industry. . In fact OTT is perfectly suited to feed very efficiently viewer main screen as well as all his companion devices
Meratech is available to design, supply, deliver and put in service turn key or partial solution to include the whole system or only part of it such as acquisition, encoding, packaging, storage, CDN, front end player, backoffice system and middleware. Post sale support contract based on SLA can be included.
IPTV
IPTV stands for “Internet Protocol Television”, a technology that delivers television content and multimedia over Internet Protocol (IP) networks. IPTV allows users to stream live TV channels and on-demand content directly to their devices, such as smart TVs, computers, smartphones, and set-top boxes. It operates through broadband internet connections, enabling interactive features like video-on-demand, time-shifting, and digital recording. IPTV works by encoding TV signals into IP packets, which are then transmitted over the internet to users’ devices. It provides a flexible and scalable solution for distributing TV content, making it increasingly popular as an alternative to traditional cable or satellite TV services.
Meratech is available to design, deliver and put in service turn key or partial solution to include the whole system or only part of it such as the video headend, the streaming system, the optical distribution, the middleware etc. Post sale support contract based on SLA can be included.
IPTV
DTH
DTH
DTH (Direct-to-Home) television is a satellite service delivering digital content directly to homes, using geostationary satellites, requiring a satellite dish, set-top box, and TV. DTH offers a wide range of channels, including regional and international options, with high-quality digital signals and stability. It’s less susceptible to disruptions from weather or obstacles. Interactive features like video-on-demand and pay-per-view are available. DTH is popular where cable infrastructure is limited, providing convenient access to diverse entertainment options.
Meratech is available to design, supply, deliver and put in service the central video headend as well as the transport system connecting the video headend with the uplink site. Post sale support contract based on SLA can be included.
VIDEO CONTRIBUTION
Video contribution refers to the process of capturing, transmitting, and delivering high-quality video content from its source location to a central point or a broadcasting center. It is used primarily in broadcasting, live events, and media production industries to gather video content from different locations and consolidate it for distribution to a wider audience. Video contribution often involves the use of dedicated fiber-optic links, satellite links, or internet-based transmission methods to ensure reliable and high-bandwidth delivery. The content gathered through video contribution is typically used for live broadcasting, news coverage, sports events, and other media production purposes, where quality and real-time delivery are essential.
Meratech is available to design, supply, deliver and put in service contribution network based on dedicated bandwidth resources (fiber, SAT RF, leased bandwidth etc.) or based on transmission across the Public Internet (SRT, RIST, Zixi etc.). Post sale support contract based on SLA can be included.
Video contribution
DVB/C/C2
DVB-C/C2 stands for “Digital Video Broadcasting – Cable and Cable 2.” It is a set of digital television standards used for the transmission of television signals over cable networks. DVB-C/C2 employs modulation techniques to deliver compressed audio and video data, allowing cable operators to offer a wide range of digital TV channels to subscribers. The C2 version is an evolution of the original DVB-C standard, providing more efficient compression and improved error correction, enabling higher data transmission rates and better video quality. DVB-C/C2 enables interactive services, electronic program guides, and high-definition broadcasting, making it a significant advancement in cable television technology.
Meratech is available to design, supply, deliver and put in service the central video headend as well as the transport system typically connecting the central video headend with regional site. Post sale support contract based on SLA can be included.
DVB/T/T2
DVB-T/T2 stands for “Digital Video Broadcasting – Terrestrial and Terrestrial 2.” It is a set of digital television standards used for the transmission of television signals over terrestrial (over-the-air) broadcast networks. DVB-T/T2 employs modulation techniques to deliver compressed audio and video data, allowing viewers with compatible receivers to access digital TV channels through standard television antennas. The T2 version is an improvement over the original DVB-T standard, offering more efficient compression, better error correction, and higher data transmission rates, enabling higher-quality video, including high-definition broadcasting. DVB-T/T2 has been widely adopted globally, facilitating the transition from analog to digital terrestrial television broadcasting.
Meratech is available to design, supply, deliver and put in service the central video headend, the regional video headend, the transmitting sites and the transport network connecting the fore mentioned sites. Post sale support contract based on SLA can be included.
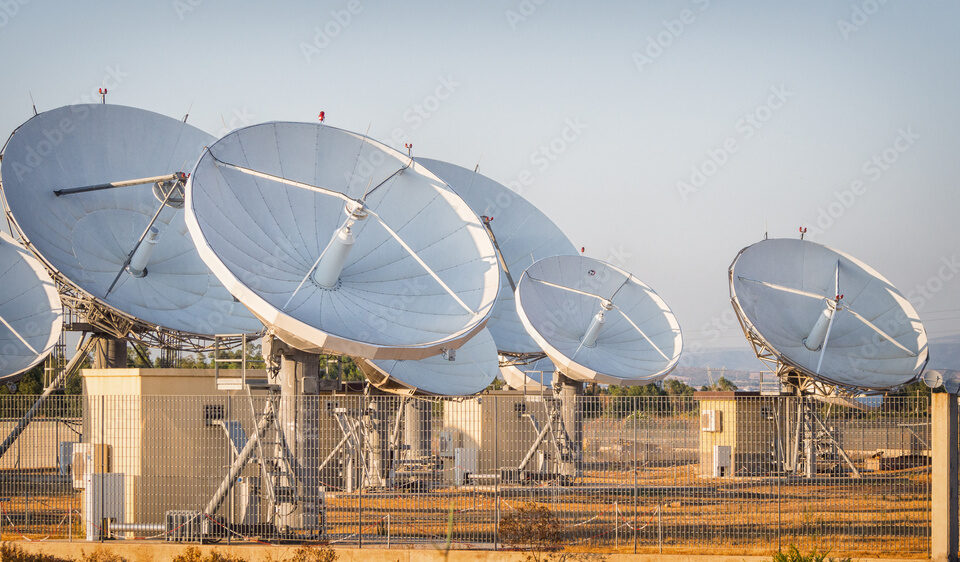
Satellite Teleport
SATELLITE TELEPORT
A Satellite Teleport is a facility that communicates with geostationary satellites to transmit and receive communication signals. It acts as a gateway between ground-based communication networks and satellites. Teleports are equipped with large parabolic antennas to establish a two-way communication link with the satellites in orbit. They handle various types of data, including television broadcasting, internet connectivity, voice communications, and corporate data exchange. Teleports are crucial for enabling satellite-based services worldwide and play a vital role in global communications infrastructure.
Meratech operate multiple downlink sites and it can offer managed service such as the reception and streaming to customer sites of out of reach TV channels. Likewise Meratech operate multiple uplink sites which can be used in support to customer operation. Post sale support contract based on SLA can be included.
MICROWAVE LINK,FIXED
Microwave Link refers to a communication system that uses microwave radio signals to transmit data, voice, or video over a line-of-sight path between two fixed locations. It is commonly employed for point-to-point communication, such as connecting two buildings, remote sites, or providing backhaul for cellular networks.
We differentiate between the fixed microwave link established between two predetermined locations (commonly used for providing high-capacity data connections, voice services, and video transmission in scenarios where laying physical cables is impractical or expensive) and mobile microwave link, which is a communication link established between a moving vehicle or platform and a fixed point (frequently used in mobile broadcasting, news gathering, and public safety applications, where real-time data and video transmission from a moving vehicle are necessary).
Meratech is available to design, supply, deliver and put in service fixed and mobile microwave links used for video transport
Microwave link
Monitoring and reporting
MONITORING & REPORTING
Monitoring and reporting in video and broadcasting involve observing and analyzing video content and transmission processes. It includes real-time surveillance of broadcast signals to ensure quality and compliance with standards. The collected data is presented in reports to aid decision-making, improve video quality, and address technical or content-related issues for a seamless viewing experience.
Meratech include monitoring and reporting as part of the deliverable in typical turn-key video system. Alternatively monitoring and reporting can be offered as managed service to any customer who operate existing video system
HOSPITALITY
Hospitality in video and broadcasting involves offering tailored video content and services to guests in hotels, resorts, or cruise ships. It includes providing live TV channels, movies, on-demand content, and interactive features for a better guest experience. The systems are designed with user-friendly interfaces, electronic program guides, and options like video-on-demand and pay-per-view. The goal is to enhance guest satisfaction, create a comfortable environment, and differentiate services from competitors, ultimately improving the overall guest experience during their stay.
Meratech is available to design, supply, deliver and put in service turn-key hospitality system. Post sale support contract based on SLA can be included.
MANAGED SERVICES
MANAGED SEVICES
Meratech in collaboration with OiV, the public network operator in Croazia, has created OVM alliance which is dedicated to provide a variety of managed services to the video industry such as:
- SAT Acquisition and streaming to your preferred location of TV channels OVM can receive in several international sites
- Headend as a service
- Video monitoring as a service